Typing in the SDK¶
The Software Development Kit supports type hints to add validation to the resulting API as well as well-defined json schemas for the automated documentation. In this tutorial we will see how we can make use of this to make the API and interactive docs easier to use.
Note
MVI entrypoints communicate with json schemas and do therefore only support json-compatible input and output, such as numericals, strings, lists and dictionaries.
Why Type Hints?¶
It is not required to use type hints for your entrypoint functions. But if they are
used they will give validation to the API, which can otherwise require a fair bit
of code. Let’s look at the hello() entrypoint that we’ve seen
a few times already, but without type hints:
from mvi import service
@service.entrypoint
def hello(name):
return f"Hello {name}"
if __name__ == "__main__":
service.run()
Without the type hint, any data type is allowed into the entrypoint. Let’s
say that an error caused a list of names to be sent to name instead of a single name
then this entrypoint would respond with "Hello ['Lars', 'Claus', 'Bob']" and a
status code of 200. We also won’t get any schema definitions in the API documentation.
Let’s define the same entrypoint again but with type hints this time:
from mvi import service
@service.entrypoint
def hello(name: str) -> str:
return f"Hello {name}"
if __name__ == "__main__":
service.run()
With the same input {"name": ['Lars', 'Claus', 'Bob']} we would get a 422 error
and the response:
{
"detail": [
{
"loc": [
"body",
"name"
],
"msg": "str type expected",
"type": "type_error.str"
}
]
}
Which tells us that the name argument expected a string, but got something else.
Note
The validation uses pydantic
behind the scenes which will try to coerce the input to the correct type,
so if we were to call hello() with the input {"name": 1} it will
convert 1 to string and respond with Hello 1. If this behaviour is not
not desirable, take a look at pydantic’s
strict types.
Creating an Input Model¶
In our examples so far we have only seen standard python types as type hints:
from mvi import service
@service.entrypoint
def example(data: dict) -> int:
pass
This makes sure that only dictionaries can be used as input for example().
But a dictionary can contain many types of data, and usually only one (or a few)
ways are expected. To simplify the life of the user, we can define something called
a data model, that we create by extending the BaseModel class from
pydantic:
class Item(BaseModel):
name: str
description: Optional[str] = None
price: float
tax: Optional[float] = None
The BaseModel
describes a JSON object (or python dict) like:
{
"name": "Foo",
"description": "An optional description",
"price": 45.2,
"tax": 3.5
}
The BaseModel helps the API to know what format the input json should
conform to. If the request body of your API call does not match the model it will
send a 422 HTTP-error with an error description.
Let’s create a new service that will convert its input into a dataframe and respond with the sum of its rows. For this we must be certain that the columns only contains floats:
>>> mvi init
project_name [my_project]: row_sum_service
Then in service.py write the following code:
import logging
from typing import List
import pandas as pd
from mvi import service
from pydantic import BaseModel
logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
class DataForm(BaseModel):
col1: List[float]
col2: List[float]
col3: List[float]
@service.entrypoint
def calculate(data: DataForm) -> list:
df = pd.DataFrame.from_dict(data.dict())
logger.info(f"Recieved data: \n{df}")
row_sum = df.sum(axis=1)
logger.info(f"Row sums: {row_sum}")
return row_sum.to_list()
if __name__ == "__main__":
service.run()
And add pydantic and pandas to requirements.txt:
va-mvi
pydantic
pandas
And deploy the new service:
>>> mvi deploy row_sum 1.0.0 ./row_sum_service
Active host: http://your-host
Deploying service...
Service deployed successfully
MAIN NAME VERSION STATUS RUNNING
------ ------- --------- -------- -----------------------------------
* row_sum 1.0.0 running Running (since 2020-11-24 10:11:37)
Now if we head on to the automated documentation at http://your-host/services/row_sum/docs you should see the following:
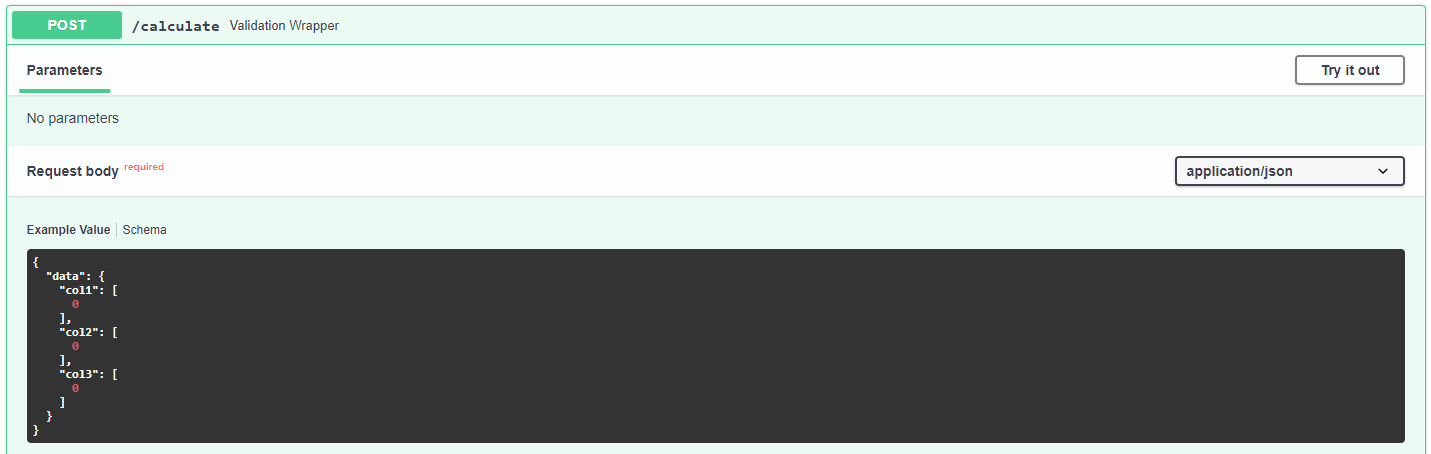
We can see that now, we have an example input ready for us in the schema view, which makes testing with the interactive docs much faster, but the most important feature we get is validation of the input. Let’s try to change the value of “col1” to “string”:
{
"data": {
"col1": "string",
"col2": [
0
],
"col3": [
0
]
}
}
And we get the response 422 Error: Unprocessable Entity:
{
"detail": [
{
"loc": [
"body",
"data",
"col1"
],
"msg": "value is not a valid list",
"type": "type_error.list"
}
]
}
Which tells us that the value of “col1” in “data” in the request body is not a valid list. If we had used no type hinting or instead used a dictionary we would not get this level of control of what data we accept into the entrypoint, which invites many bugs due to data validation issues.
Custom Validation¶
We’ve seen how a data model can be used to ensure that the input data types are
validated, but sometimes it’s not strict enough. Let’s take the hello service
as an example this time. The hello() function takes any string as it’s
input <name> and then returns “Hello <name>”. But we do not want the user to input
numbers as name, so we want to add validation for that, so we create a base model
for the the user name:
from pydantic import BaseModel, validator
class NameModel(BaseModel):
name: str
@validator("name")
def must_not_be_numeric(cls, name):
if name.isnumeric():
raise ValueError(
"Names cannot be numeric!"
)
return name
The validator() decorator from pydantic allows us to define classmethods
that can run arbitrary code on the data input and raise exceptions if it violates
the desired format.
On the input name “123”, which is a number, we expect the validation to kick in:
{
"data": {
"name": "123"
}
}
And we get a response 422 Error: Unprocessable Entity, which is exactly what we wanted:
{
"detail": [
{
"loc": [
"body",
"data",
"name"
],
"msg": "Names cannot be numeric!",
"type": "value_error"
}
]
}
Schema Example¶
You can add example inputs for the documentation to
speed up testing. To do this we create a local class Config
within the data model:
class NameModel(BaseModel):
name: str
class Config:
schema_extra = {
"example": {
"name": "Kermit"
}
}
This would change the standard value in the schema example to “Kermit”.
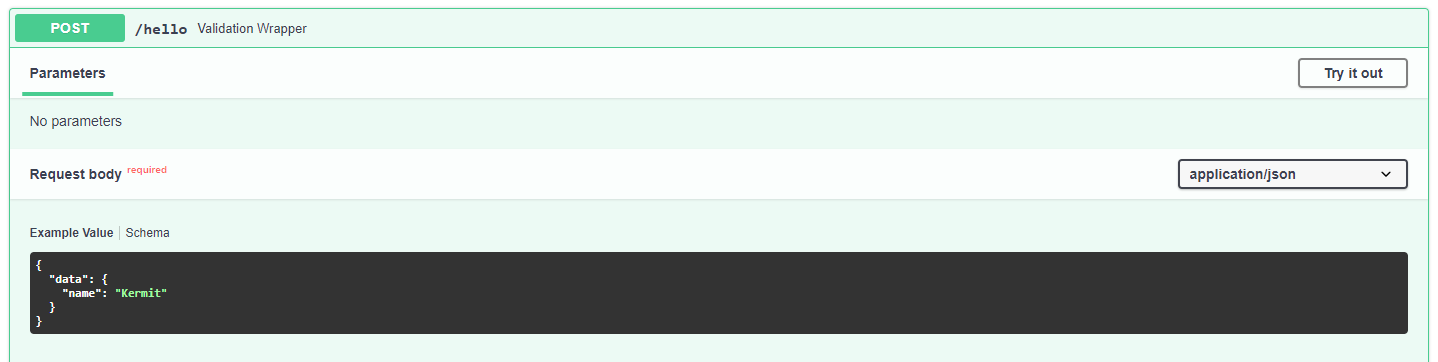
Using Non-jsonable Data Types¶
Some data types like numpy.ndarray and pandas.DataFrame are very common for
e.g. data science, but are not natively supported by Pydantic. They must first be
converted to a json-compatible format like lists for arrays and dictionaries for
dataframes. This can be made more or less automated by using type hints with
custom classes. MVI includes input and output types for numpy.ndarray and
pandas.DataFrame. Let’s look at how they can be used:
from mvi import service
from mvi.data_types import ArrayInput, ArrayOutput
@service.entrypoint
def array_sum(array1: ArrayInput, array2: ArrayInput) -> ArrayOutput:
return array1 + array2
if __name__ == "__main__":
service.run()
Trying out this entrypoint with the input {"array1": [1, 2, 3], "array2": [4, 5, 6]}
responds with [5, 7, 9]. If we had used lists as type hints they would
have been concatenated to [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]. The ArrayInput
class has a validator that converts its input to numpy arrays and conversely,
ArrayOutput has a validator that converts the array to a list.
Let’s take a look at how ArrayInput and
ArrayOutput are defined so you can make your own Pydantic
compatible data types:
class ArrayInput(np.ndarray):
"""Pydantic compatible data type for numpy ndarray input."""
@classmethod
def __get_validators__(cls):
yield cls.validate
@classmethod
def __modify_schema__(cls, field_schema):
field_schema.update(type="array", items={})
@classmethod
def validate(cls, value: List) -> np.ndarray:
# Transform input to ndarray
return np.array(value)
class ArrayOutput(np.ndarray):
"""Pydantic compatible data type for numpy ndarray output."""
@classmethod
def __get_validators__(cls):
yield cls.validate
@classmethod
def __modify_schema__(cls, field_schema):
field_schema.update(type="array", items={})
@classmethod
def validate(cls, value: np.ndarray) -> List:
# Transform ndarray to list for output
return value.tolist()
Pydantic looks for the __get_validators__() method to see if the class has a
validator method, in this case validate() that takes a value and returns a value.
For the input, the value must be a json-compatible type, that should then be converted to the
type you want to use in your entrypoint and for the output it should be converted back to
the json-compatible representation.
The __modify_schema__() method is let’s pydantic create a schema for for the data
type. It takes an argument for the field_schema which should be modified in-place. Take a
look at JSON Schema Types
that pydantic supports to find which schema fits you data type.
Note
Using ArrayInput and
dataFrameInput as input type can be likened to using
list or dict and doesn’t give as much control of the validation as the
pydantic models. So in some cases it might be better to use pydantic and convert
the data inside of the entrypoint.